For seven years in a row, data scientist has been been listed as one of the top three best jobs in the U.S., according to Glassdoor. What’s more, our analysis of job posting data shows that the demand for data science skills will drive a 41.9 percent rise in employment in the field through 2031. Not only is there a huge demand, but there’s also a noticeable shortage of qualified data scientists.

Daniel Gutierrez, managing editor of insideBIGDATA, told Forbes, “The word on the street is there’s definitely a shortage of people who can do data science.” If you have a passion for computers, math, and discovering answers through data analysis, then earning an advanced degree in data science or data analytics might be your next step.
What is Data Science?
Martin Schedlbauer, PhD and data science professor at Northeastern University, says that data science is used by “computing professionals who have the skills for collecting, shaping, storing, managing, and analyzing data [as an] important resource for organizations to allow for data-driven decision making.” Almost every interaction with technology includes data—your Amazon purchases, Facebook feed, Netflix recommendations, and even the facial recognition required to sign in to your phone.
Computer Science vs. Data Science: Which is Right for You?
Download our free guide to explore career opportunities in computer and data science.
Why Is Data Science Important?
1. Provides a Personalized User Experience
Amazon is a prime example of just how helpful data collection can be for the average shopper. Amazon’s data sets remember what you’ve purchased, what you’ve paid, and what you’ve searched. This allows Amazon to customize its subsequent homepage views to fit your needs. For example, if you search camping gear, baby items, and groceries, Amazon will not spam you with ads or product recommendations for geriatric vitamins. Instead, you are going to see items that may actually benefit you, such as a compact camping high chair for infants.
Learn More: Data Analytics vs. Data Science: A Breakdown
Similarly, data science can be useful for reminding you of habitual purchases. If you order diapers every month, for example, you might see a strategically placed coupon or deal around the same time each month. This use of data is meant to act as a trigger, prompting you to think, “I just remembered I need to buy diapers, and I should buy them now because they are on sale.”
2. Saves Money for Both Consumers and Companies
Data science benefits both companies and consumers alike. McKinsey Global Institute found that big data can increase a retailer’s profit margin by 60 percent, and “services enabled by personal-location data can allow consumers to capture $600 billion in economic surplus,” meaning they are able to purchase a good or service for less than they were expecting. For example, if you budgeted $7,500 to purchase a jacuzzi and then found the exact model you wanted for $6,000, your economic surplus would be $1,500. Data science can simultaneously increase retailer profitability and save consumers money, which is a win-win for a healthy economy.
3. Improves Public Health
Data science doesn’t just enable retailers to influence our purchasing habits—its importance extends much further.
Data science can improve public health through wearable trackers that motivate individuals to adopt healthier habits and can alert people to potentially critical health issues. Data can also improve diagnostic accuracy, accelerate finding cures for specific diseases, or even stop the spread of a virus.
When the Ebola virus outbreak hit West Africa in 2014, scientists were able to track the spread of the disease and predict the areas most vulnerable to the illness. This data helped health officials get in front of the outbreak and prevent it from becoming a worldwide epidemic.
4. Benefits Almost Every Industry
Data science has critical applications across most industries. For example, data is used by farmers for efficient food growth and delivery, by food suppliers to cut down on food waste, and by nonprofit organizations to boost fundraising efforts and predict funding needs.
In a 2015 speech, Economist and Freakonomics author Steven Levitt said that CEOs know they are missing out on the importance of Big Data, but they do not have the right teams in place to perform the skills. He says, “I really do believe still that the combination of collaborations with firms’ big data and randomization […] is absolutely going to be at the center of what economics is and what other social sciences are going forward.”
Pursuing a career in data science is a smart move, not just because it’s trendy and pays well, but because data very well may be the pivot point on which the entire economy turns.
In-Demand Data Science Careers
Data science experts are needed in virtually every job sector—not just technology. In fact, the five biggest tech companies—Google, Amazon, Apple, Microsoft, and Facebook—only employ one-half of one percent of U.S. employees. In order to break into these high-paying, in-demand roles, an advanced education is generally required.
“While there are notable exceptions, a very strong educational background is usually required to develop the depth of knowledge necessary to be a data scientist,” reports KDnuggets, a leading site on Big Data.
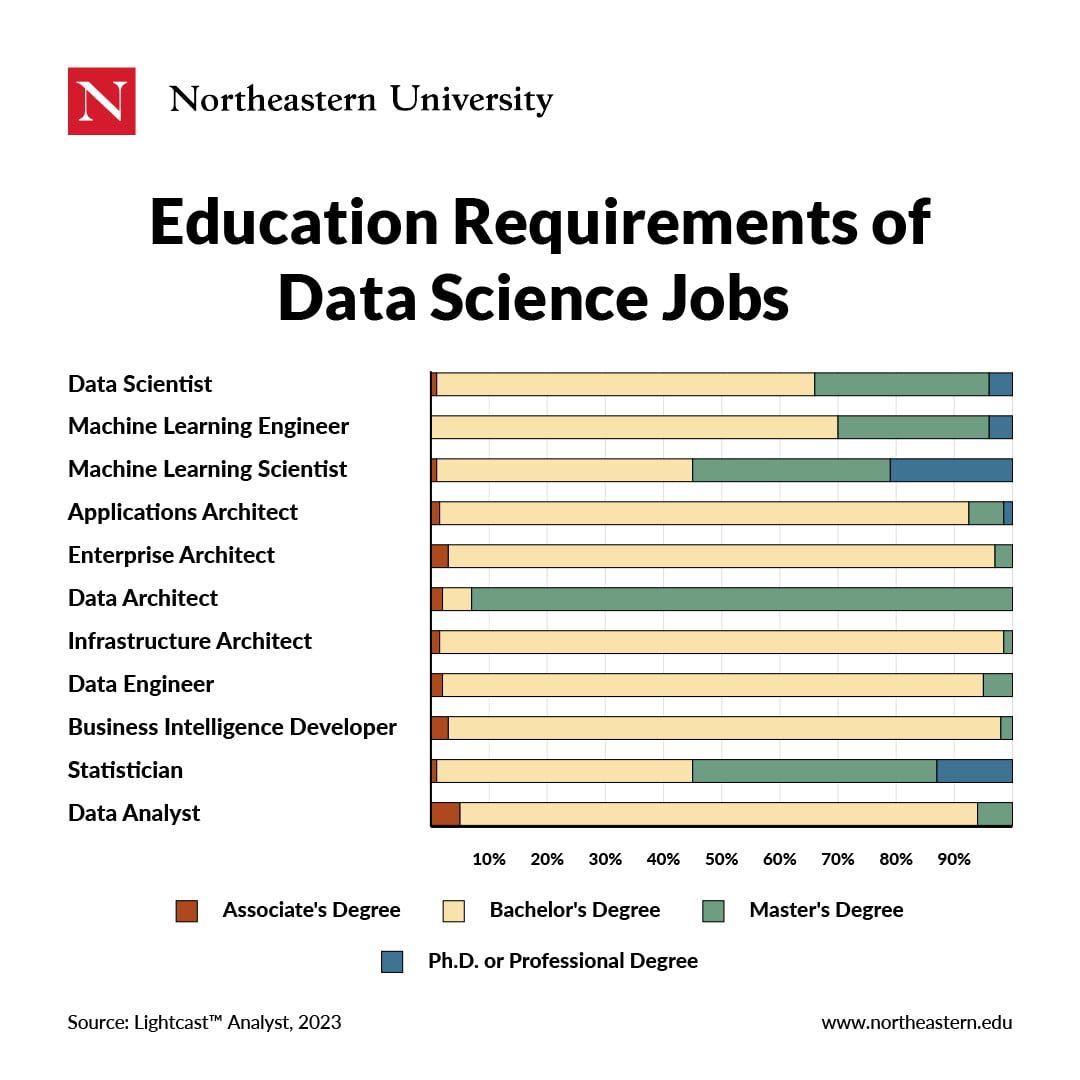
Here are some of the leading data science careers you can break into with an advanced degree.

1. Data Scientist
Average Salary: $123,300
Typical Job Requirements: Find, clean, and organize data for companies. Data scientists need to be able to analyze large amounts of complex raw and processed information to find patterns that benefit an organization and help drive its strategic business decisions. Compared to data analysts, data scientists are much more technical.
Learn more: What Does a Data Scientist Do?
2. Machine Learning Engineer
Average Salary: $150,300
Typical Job Requirements: Machine learning engineers create data funnels and deliver software solutions. They typically need strong statistics and programming skills, as well as a knowledge of software engineering. In addition to designing and building machine learning systems, they’re also responsible for running tests and experiments to monitor the performance and functionality of such systems.
3. Machine Learning Scientist
Average Salary: $135,000
Typical Job Requirements: Research new data approaches and algorithms to be used in adaptive systems including supervised, unsupervised, and deep learning techniques. Machine learning scientists often go by titles like Research Scientist or Research Engineer.
4. Applications Architect
Average Salary: $146,200
Typical Job Requirements: Track the behavior of applications used within a business and how they interact with each other and with users. Applications architects are focused on designing the architecture of applications as well, including building components like user interface and infrastructure.
5. Enterprise Architect
Average Salary: $150,400
Typical Job Requirements: An enterprise architect is responsible for aligning an organization’s strategy with the technology needed to execute its objectives. To do so, they must have a complete understanding of the business and its technology needs in order to design the systems architecture required to meet them.
6. Data Architect
Average Salary: $137,000
Typical Job Requirements: Ensure data solutions are built for performance and design analytics applications for multiple platforms. In addition to creating new database systems, data architects often find ways to improve the performance and functionality of existing systems, as well as working to provide access to database administrators and analysts.
7. Infrastructure Architect
Average Salary: $145,200
Typical Job Requirements: Oversee that all business systems are working optimally and can support the development of new technologies and system requirements. A similar job title is Cloud Infrastructure Architect, which oversees a company’s cloud computing strategy.
8. Data Engineer
Average Salary: $129,900
Typical Job Requirements: Perform batch processing or real-time processing on gathered and stored data. Data engineers are also responsible for building and maintaining data pipelines that create a robust and interconnected data ecosystem within an organization, making information accessible for data scientists.
9. Business Intelligence (BI) Developer
Average Salary: $105,300
Typical Job Requirements: BI developers design and develop strategies to assist business users in quickly finding the information they need to make better business decisions. Extremely data-savvy, they use BI tools or develop custom BI analytic applications to facilitate the end-users’ understanding of their systems.
10. Statistician
Average Salary: $87,300
Typical Job Requirements: Statisticians collect, analyze, and interpret data in order to identify trends and relationships which can be used to inform organizational decision-making. The daily responsibilities of statisticians often include designing data collection processes, communicating findings to stakeholders, and advising organizational strategy.
Learn More: What Do Statisticians Do?
11. Data Analyst
Average Salary: $80,800
Typical Job Requirements: Transform and manipulate large data sets to suit the desired analysis for companies. For many companies, this role can also include tracking web analytics and analyzing A/B testing. Data analysts also aid in the decision-making process by preparing reports for organizational leaders which effectively communicate trends and insights gleaned from their analysis.
Learn More: What Does a Data Analyst Do?
Data Scientists Are in Constant Demand
Schedlbauer concludes that while some data science work will likely be automated within the next 10 years, “there is a clear need for professionals who understand a business need, can devise a data-oriented solution, and then implement that solution.”
Data science experts are needed in almost every field, from government security to dating apps. Millions of businesses and government departments rely on big data to succeed and better serve their customers. Data science careers are in high demand and this trend will not be slowing down any time soon, if ever.
Breaking Into the Field
If you want to break into the field of data science, there are a number of ways you can prepare yourself to take on these challenging yet exciting roles. Perhaps most importantly, you will need to impress future employers by demonstrating your expertise and previous work experience. Our analysis of job postings data shows that approximately 37 percent of job postings for the previously listed positions are entry-level—three or less years of experience required.
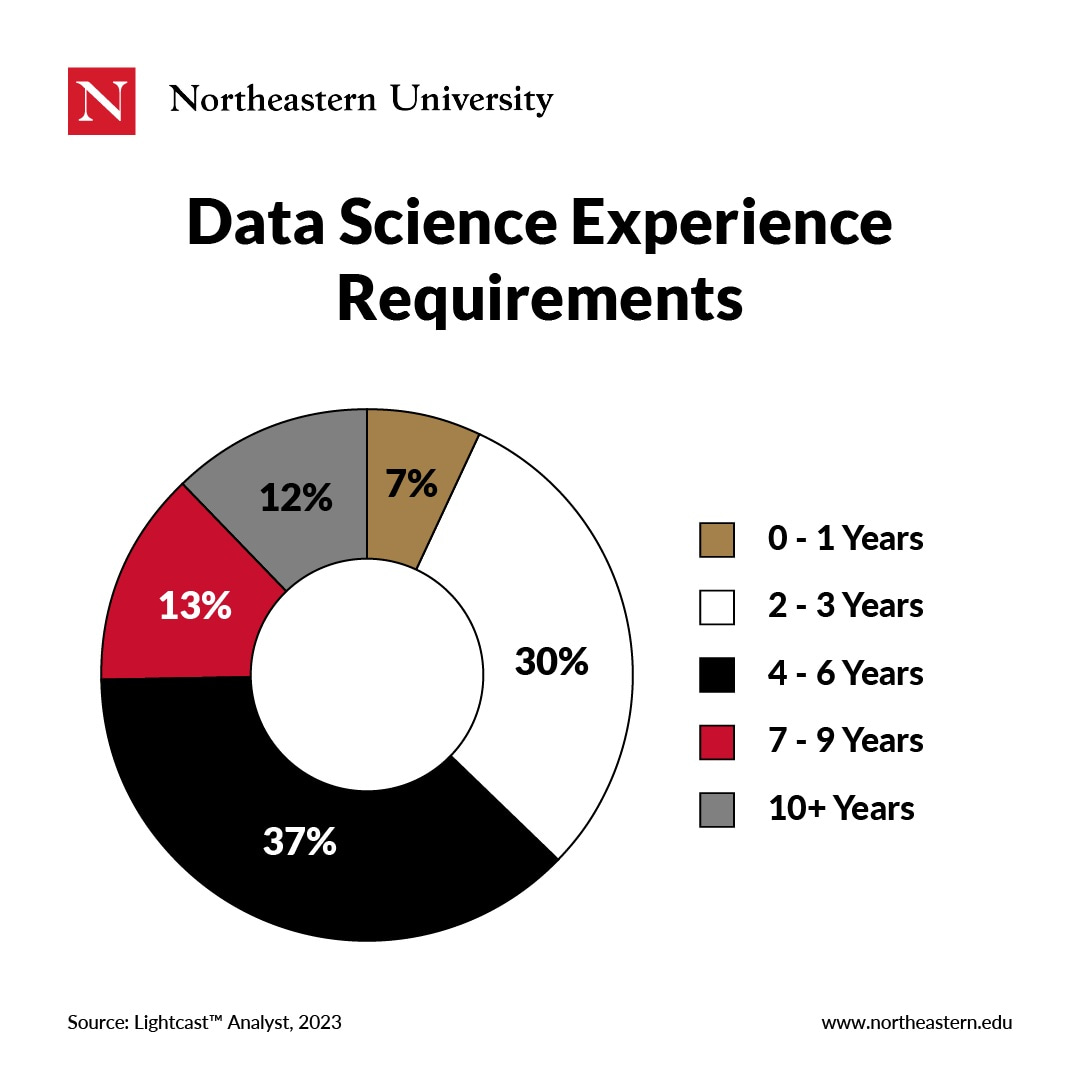
One way you can build those skills and experience is to pursue an advanced degree program in your area of interest.
While the majority of data science positions require a bachelor’s degree at minimum, many still prefer Master’s-level applicants. For this reason, pursuing a Master’s degree can set you apart from the competition, compensate for a lack of experience, and increase your earning potential.
Northeastern University, for example, offers master’s degree programs in both data science and data analytics which are designed to develop the skills that employers are seeking. Both programs also provide students with the opportunity to participate in co-ops and experiential learning experiences, allowing them to build hands-on experience prior to graduating. Once you have considered factors like your personal background, interests, and career aspirations, you will be able to determine which degree program is right for you and take the next step towards achieving your goals.
Editor’s note: This article was originally published in June 2020 and has since been updated for accuracy.






Related Articles
Is a Data Analytics Bootcamp Worth It?
What is Learning Analytics & How Can it Be Used?
Why This Alum Decided to Earn His Master’s Degree in Computer Science