Microorganisms may be invisible to the naked eye, but they play a big role in public and environmental health. If you’re interested in the biological sciences, working as a microbiologist offers the opportunity to experiment with the earth’s tiniest living things to solve some of the world’s biggest problems.
Here’s everything you need to know about microbiology, the top required skills for microbiologists to stay competitive in this field, and how you can develop these competencies.
What Is Microbiology?
Microbiology is the study of microscopic organisms and their life processes. Microorganisms, such as bacteria, viruses, and fungi are living things that grow in our environment and the bodies of other organisms. Microorganisms are an important part of the earth’s ecosystems, having both negative and positive effects on the health of other living things.

Microbiologists experiment with microbes to better understand how they function and interact with other entities. This bioinformatics career path researches various ways to manage microbes and reduce their harmful effects while also discovering new ways they can be used to improve quality of life.
Prospective microbiologists interested in making these groundbreaking discoveries need the necessary skills to excel in the field.
Top 10 Required Skills For Microbiologists
Microbiology is a complex job that involves hands-on lab work, collaboration, and exploratory research. While a degree in bioinformatics is the most important step when pursuing this career path, you’ll also need technical and interpersonal skills to land the most competitive positions.
Here are the top 10 skills employers are looking for in microbiology job postings.

1. Microbiology
A strong foundation in microbiology is essential. Core skills include the ability to classify microorganisms and monitor their responses to different stimuli or environmental conditions. You’ll need to know how to maintain bacterial cultures to study their development and how to handle different microorganisms safely to prevent contamination or public health risks. Microbiologists also diagnose infections or illnesses related to microorganisms, so it’s crucial to understand how microbes affect other organisms.
2. Biology
Biology is the basis for all life sciences and an integral part of any microbiology degree program. To identify and classify different types of organisms, you need extensive knowledge of the cell biology of plants, animals, and insects. You also need to observe their habits and characteristics, such as how organisms behave, what they consume, and how they recharge. A clear understanding of all living things and their ecosystem relationships is essential to developing solutions as a microbiologist.
3. Good Manufacturing Practices
Knowledge of safe handling, storage, testing, and processing practices is vital in industries such as pharmaceuticals and food production. Since microorganisms can often degrade or contaminate these products, manufacturers need well-controlled operations to reduce the risk of public health threats as much as possible. Microbiologists can assist in manufacturing quality control by designing processes that ensure safety. Obtaining a Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) certification is the best way to demonstrate proficiency in this skill to prospective employers.
4. Communications
Effective communication is one of the most essential soft skills needed to become a microbiologist. Not only do microbiologists need to collaborate with other researchers and biological technicians, but they also need to write frequent reports, articles, and other communications. Depending on the industry and work environment, microbiologists must also interact with administrators, engineers, regulators, physicians, and the public. The ability to clearly express findings and recommendations can take microbiologists far in the field.
5. Quality Control
Quality control expertise is an excellent skill to obtain as a microbiologist because it often leads to more career opportunities. Microbiologists with this competency can work in settings such as diagnostic laboratories, biotechnology companies, or environmental agencies. They ensure consistent quality standards by developing effective protocols, documenting procedures, maintaining sterile environments, and verifying the safety of all products.
6. Environmental Monitoring
Microbiologists who work in environmentally focused roles are often responsible for testing and assessing conditions in controlled areas. They collect samples, such as air, water, and soil from various environments to identify pathogens and make recommendations on how to improve environment quality. Organizations also rely on microbiologists to measure the impact of business activities on surrounding environments. This skill can be particularly valuable to individuals interested in working in environmental science.
7. Management
If you’re interested in running a laboratory or managing a team of researchers, management skills are essential to career advancement. Lab managers must be skilled at coordinating projects and resources and choosing the right processes and technologies to achieve their goals. Employers want leaders who have a mastery of leadership and technical problem-solving to ensure they are well equipped to train and direct biological technicians.
8. Investigation
Research and experimentation are the backbone of microbiology. Monitoring studies and correlating data is a substantial part of any career in microbiology; therefore, observation skills are a must. In the bioinformatics field, this often means some form of data analysis. According to Jared Auclair, associate dean of Professional Program and Graduate Affairs in the College of Science at Northeastern University, “One of the most important skills is experience with data analysis tools that analyze microbiology information. There’s a lot of data collected, but not a lot of people know how to analyze and streamline it. So there’s an opportunity there.”

9. Operations
Microbiologists who eventually want to work in higher-level roles should focus on building operations management and analysis skills. Learning to balance all operational factors in business and research enables microbiologists to make efficient decisions about quality control, workflow management, systems and equipment maintenance, compliance, and staffing.
10. Microbiological Testing
Biological technicians have to be up to date on microbiological testing methods in their industry. Both state and federal laws dictate testing standards, which constantly evolves as a result of a boost in available research. Microbiologists must be able to conduct accurate tests, interpret results, and, when necessary, recommend changes to current policies.
How to Develop Your Microbiology Skills
These competencies may seem intimidating, but advancing your education is one method to develop these skill sets. For example, earning a master’s degree is one of the best ways to advance your career and gain a well-rounded skill set that is sure to impress prospective employers.
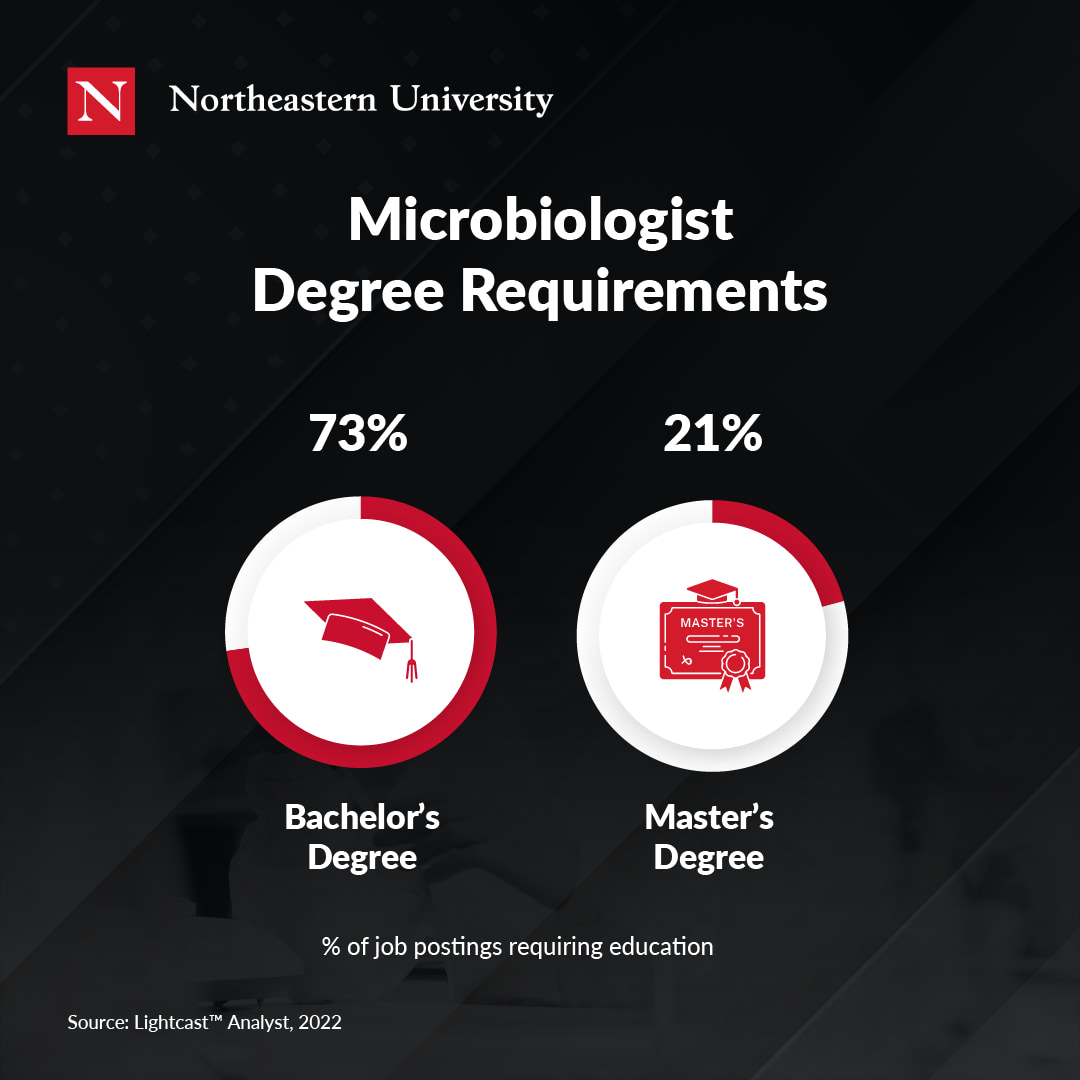
For individuals who want experience with these bioinformatic competencies, experiential learning programs offer hands-on demonstrable experience and training alongside industry experts. By combining classroom instruction with simulated professional projects, experiential learning gives graduates the opportunity to solve realistic business problems. In some experiential master’s programs, like the programs at Northeastern University, students work directly with sponsoring organizations to acclimate to the possible challenges and responsibilities they’ll face in a work environment post-gradation.
Jumpstart Your Career in Microbiology
A career in microbiology offers many rewarding opportunities to help others. With numerous leadership opportunities and various science-related career paths that require the same skill set, there is plenty of room for job growth. By obtaining a Master of Science in Bioinformatics, you can enhance your qualifications and show your commitment to expanding your skills and knowledge in the field.
If you’re interested in learning more about how to become a microbiologist, check out our MS in Biotechnology program at Northeastern University.






Related Articles
Compliance Specialists: Who They Are and What They Earn
Science or Science Fiction? The Future of Personalized Medicine
In-Demand Biotechnology Careers Shaping Our Future